VRF Context in NSX Advanced Load Balancer
Overview
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) IP technology allows users to configure multiple routing table instances to simultaneously co-exist within the same router.
VRF contexts in NSX Advanced Load Balancer enable the assignment of NSX Advanced Load Balancer service engine data interfaces to multiple VRFs. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer platform helps each VRF network achieve the target level of performance and increases network security.
This article explains the creation of VRF contexts in NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
Creating VRF Contexts
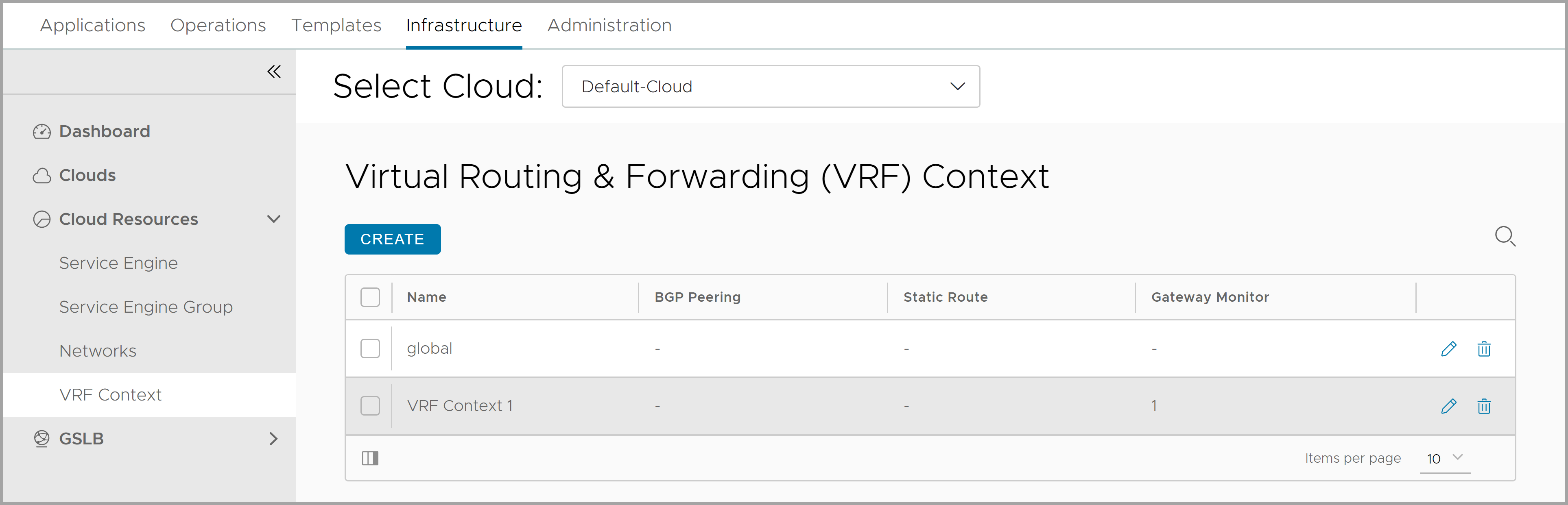
By default, NSX Advanced Load Balancer has the global VRF context created. To create a VRF Context,
- From the NSX Advanced Load Balancer UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Cloud Resources > VRF Context.
-
Click Create to open the CREATE VRF CONTEXT screen.
-
Enter a Name for the VRF Context.
- Configure Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) to enable networking peers on each end of a link to quickly detect and recover from a link failure.
-
Enter default Detection Multiplier to be used for BFD.
-
Enter the minimum rate at which the packets are sent (in milliseconds) in the Minimum Transmit Interval
-
Enter the minimum rate at which the packets are received (in milliseconds) in the Minimum Receive Interval.
-
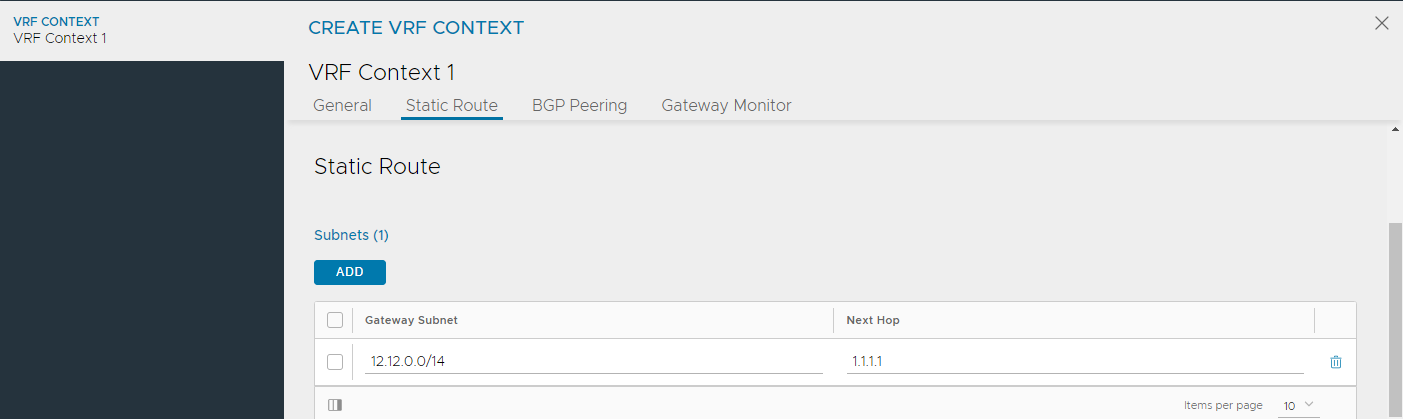
- Click Add to configure Static Routes
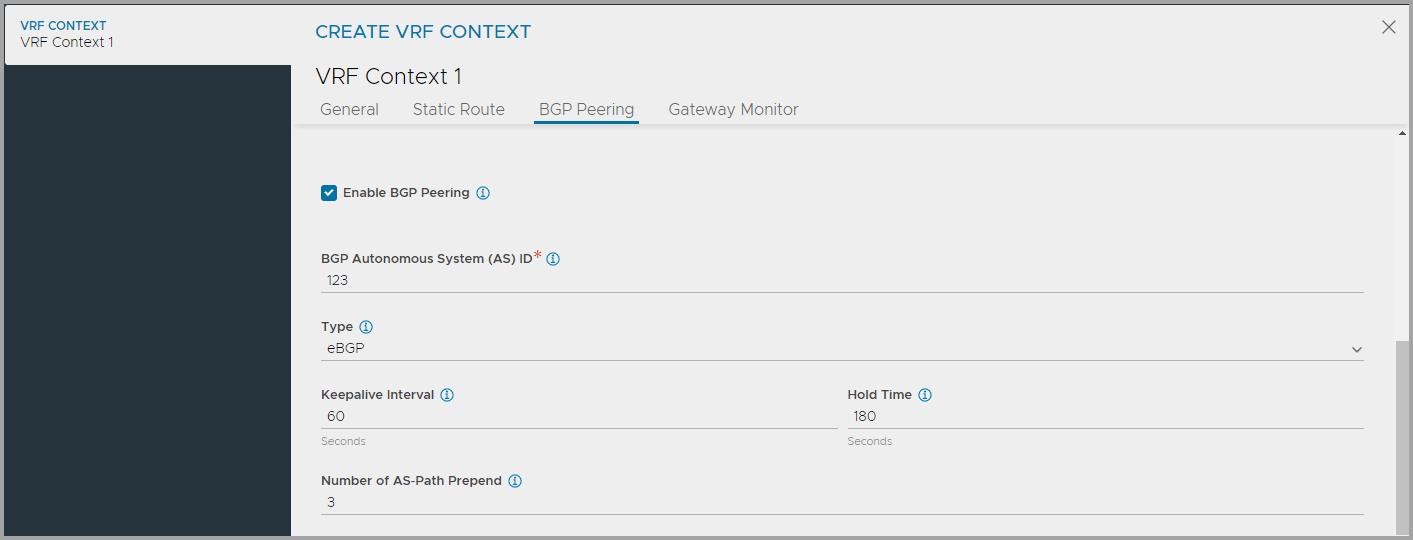
- Check Enable BGP Peering box to configure BGP local and peer details.
-
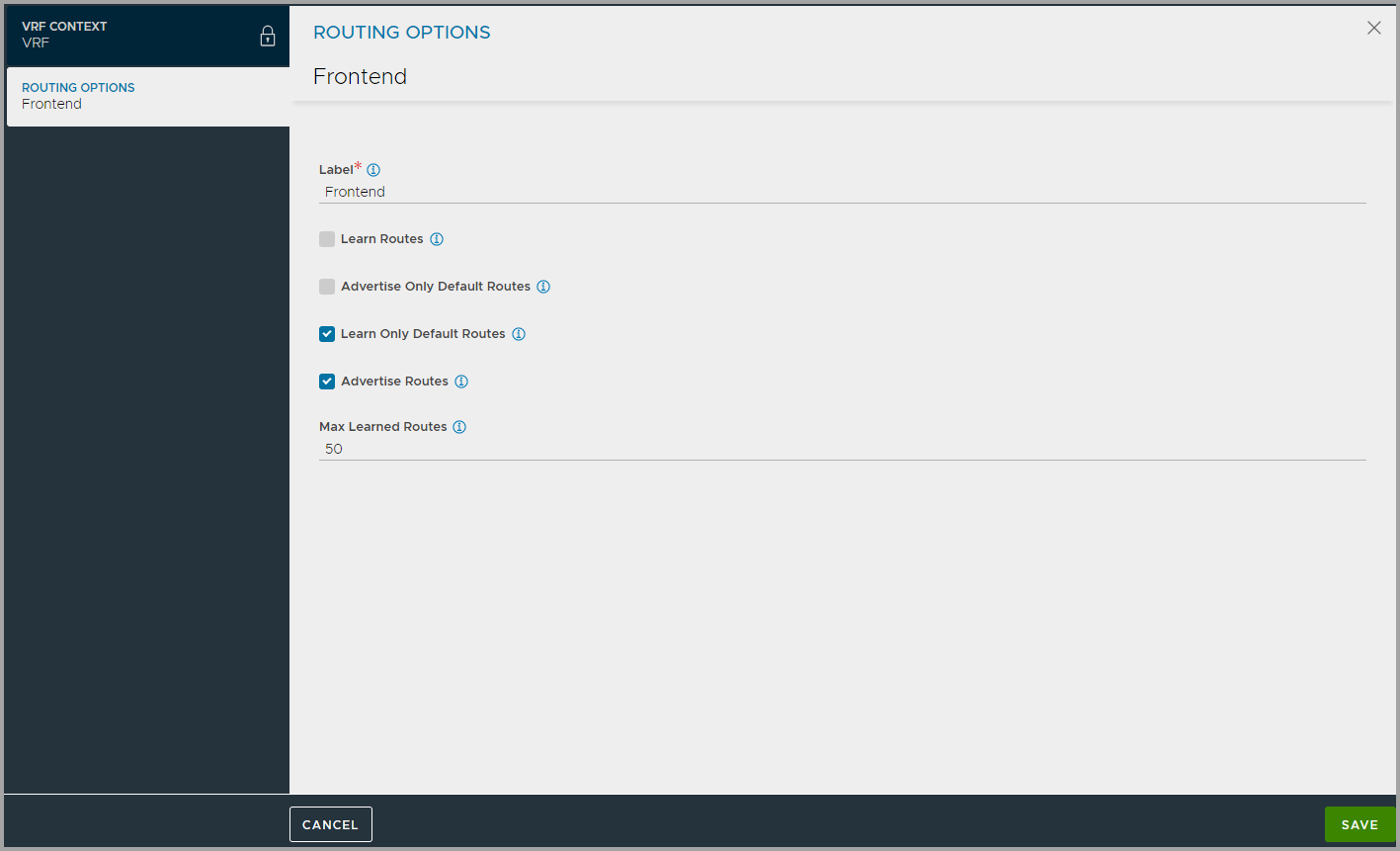
Under Routing Options click Add to configure learning and advertising options for BGP Peers.
-
Under Peers, click Add and configure the details as shown below:
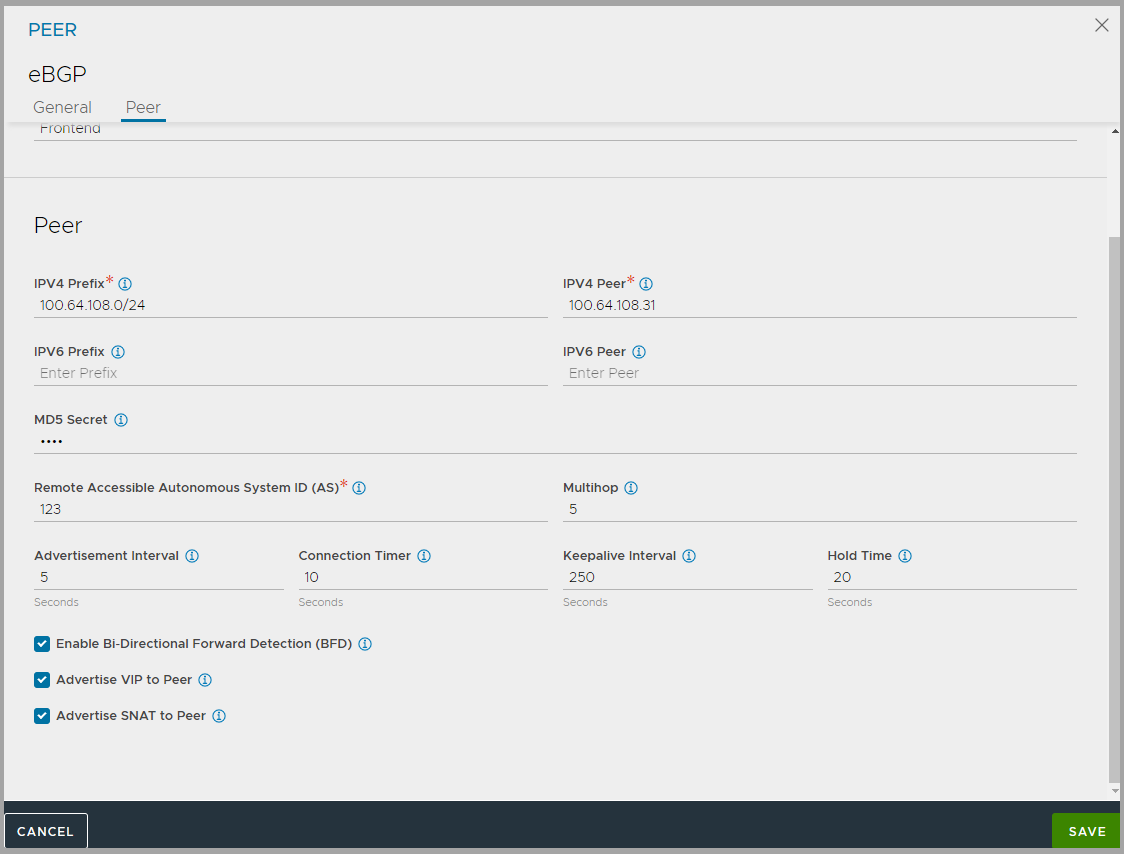
-
Click Add under Community Strings and enter either in
aa:nnformat where aa, nn is within [1,65535] orlocal-AS|no-advertise|no-export|internetformat.
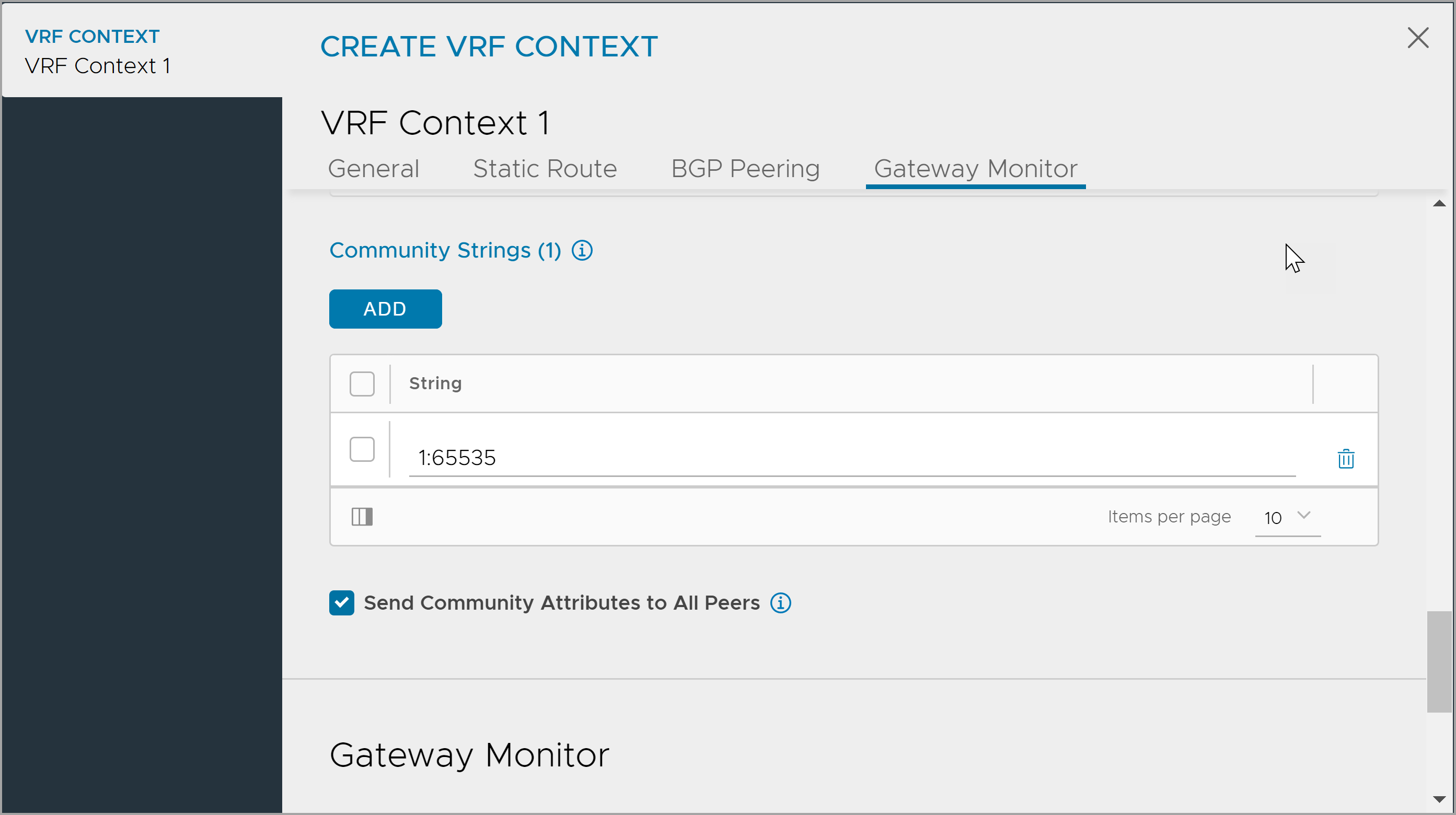
- Click Save.
The VRF context is displayed as shown below: