Virtual Server Definition
Compared to a dedicated server, a virtual server shares software and hardware resources with other operating systems (OS). Virtual servers are common because they can provide more efficient resource control and are cost-effective through server virtualization.
Traditionally, a physical server is dedicated to a specific task or application with its full processing power. Multiple physical servers require space, power, and money to maintain.
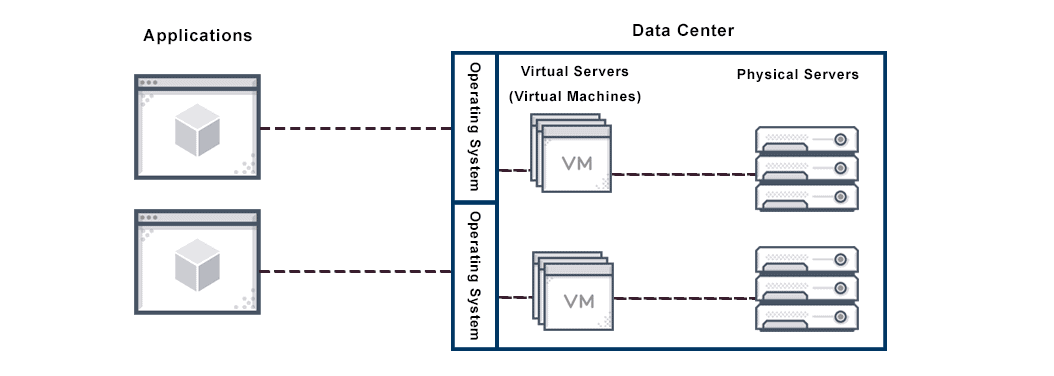
What is a Virtual Server?
A virtual server mimics the functionality of a physical dedicated server. Multiple virtual servers may be implemented on a single bare metal server, each with its own OS, independent provisioning, and software. A virtual machine server uses virtual infrastructure, virtualization software and abstracts the physical server’s computer resources to create virtual environments.
Benefits of virtual servers include faster provisioning of applications and resources, improved disaster recovery and business continuity, and minimized or eliminated downtime. Virtualization also increases IT productivity, agility, efficiency, and responsiveness. Additional benefits of virtual servers include reduced operating costs and capital, and simplified data center management.
Virtual server environments also mimic dedicated server environments in terms of how they maintain passwords and security systems. Virtual server hosting is less expensive than data center maintenance, and server software installation provisioning may further reduce web hosting costs.
Resource hogging is the most frequent of the potential problems with virtual servers. This happens when an overflow of virtual servers in a physical machine causes some virtual servers to overuse resources, leading to performance issues. However, this resource issue is avoidable with appropriate implementation.
To achieve efficiency, administrators use special server virtualization software to divide one physical dedicated server into multiple virtual servers. Converting one physical server into multiple virtual servers makes better use of power and resources. This in turn enables each physical server to efficiently run multiple OS and applications.
What is the Difference Between a Physical Server vs Virtual Server?
Technically, a virtual server exists only as a partitioned space inside a physical server. For users, there is little difference. Practically, though, there is a series of benefits to server virtualization, discussed below.
What is Server Virtualization?
Server virtualization is using virtualization software to partition or divide up the server so that it looks and functions like multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server can then run their own OS, and be used as needed. This way, the server as a whole can be used in many ways and optimized rather than being dedicated to just one application or task.
What are Server Virtualization Benefits and Challenges?
Benefits of server virtualization include:
- Cost-effective. By partitioning servers the supply of servers increases dramatically at almost zero cost.
- Resource isolation. Independent user environments ensure that things like software testing don’t affect all users.
- Save energy and space. Fewer servers mean less power consumed and less space storing them.
Resource hogging is the most common server virtualization challenge. Too many virtual servers will crowd a physical server and hurt performance.
What is a Virtual Private Server?
A virtual private server (VPS) is a virtual server that is a dedicated/private server from the user’s perspective, although a shared physical computer running multiple operating systems is running each virtual server. A VPS is also sometimes called a virtual dedicated server (VDS). Both a VPS and a VDS are types of virtual servers.
What is the Difference Between Virtual Server vs Cloud Hosting?
The primary difference between virtual servers and cloud hosting environments is that a virtual server is created for one user, while cloud hosting is designed for many users.
What is the Difference Between Virtual Desktop and Virtual Server?
Virtual servers and virtual desktops can achieve some of the same server virtualization goals for your computer network in practice, although they are not the same thing.
A virtual desktop is technology that allows different users to run different operating systems on one computer, work apart from the physical machine, or sever connected devices should one be lost or stolen.
A virtual server may still allow remote users to work and run different OSs, but it also has additional capabilities. For example, a virtual server can be used to test new software or applications without bringing down an entire server, and this is not the role of the virtual desktop.
A virtual desktop server is a form of virtual desktop infrastructure. This kind of virtual server is used to create a virtual desktop environment to host multiple virtual desktops on a virtual server designed for this purpose.
Does Avi Offer Load Balancing for Virtual Server Environments?
Yes. Avi uses software-defined principles to deliver advanced load balancing for virtual server environments. Avi Networks’ Software Load Balancer provides scalable application delivery across any infrastructure. Avi provides 100% software load balancing to ensure a fast, scalable and secure application experience for virtual server environments.
For more on the actual implementation of load balancing, security applications and web application firewalls check out our Application Delivery How-To Videos.
For more information on load balancing for virtual servers see the following resources: